Slope
In past lessons we have already learnt many facts about the slope. It is essentially a measurement of the steepness of a line. In the equation \(y = m(x)+b\), \(m\) is the slope.
Types of Slope (+/-, 0, undefined)
| A positive slope means that two variables are positively related; that is, when \(x\) increases, so does \(y\), and when \(x\) decreases, \(y\) also decreases. | 
|
| A negative slope means that two variables are negatively related; that is, when \(x\) increases, \(y\) decreases, and when \(x\) decreases, \(y\) increases. | 
|
| A slope of zero is a horizontal line. That means that there is a constant relationship between \(x\) and \(y\). The value of \(y\) does not change when \(x\) changes. These equations are written as \(y=b\) where \(b\) is the y-intercept. | 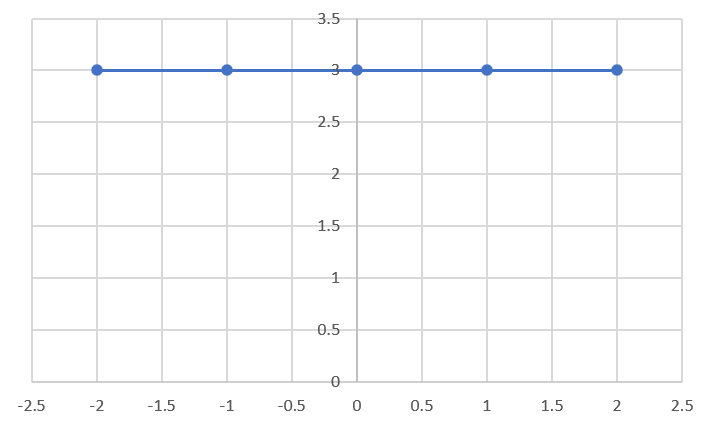
|
| An undefined slope (or an infinitely large slope) is the slope of a vertical line. The value of \(x\) does not change when y changes. These equation are usually written as \(x = a\) where \(a\) is the x-int. | 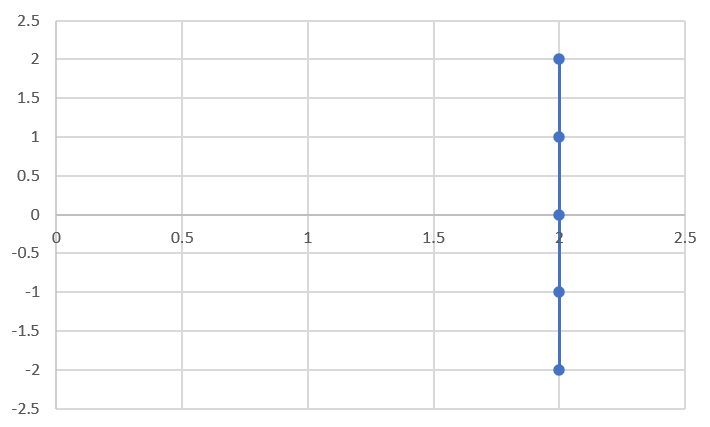
|
Slope Equation
To calculate the slope using two points on the line, we need to calculate the rise over the run. The rise is how much the line increases in the \(y\)-direction between two points. The run is the distance between the points in the \(x\)-direction between two points.
This formula calculates the change in \(y\) (the rise) divided by the change in \(x\) (run) to measure the steepness (slope). First, select two points. Then plug the \(x\) and \(y\)-values into the formula to calculate the slope.
Let's try an example using the graph below:

From looking at the graph, we can identify our first point as \( (x_1 = 1,y_1 = 3) \) and our second point as \( (x_2 = 2,y_2 = 7) \). Now, we can plug these points into the formula to determine the slope :
\(m = \cfrac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1}\)
\(m = \cfrac{7 - 3}{2 - 1}\)
\(m = \cfrac{4}{1}\)
\(m = 4\)
We can determine that the slope of the line is \(m = 4\).
The slope of a line is constant meaning it doesn't matter which two points you pick, the slope will be the same! If we calcualte the slope using the points \( (x_1 = 1,y_1 = 3) \) and \( (x_2 = 0,y_2 = -1) \) we will get the same slope.
| x Values | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y Values | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
In order to calculate the slope, we need to pick \(2\) points and plug the values into the slope formula. Note that you can pick any two points. The slope will be the same!
Let's use \( (x_1 = 6,y_1 = 10)\) and \((x_2 = 8,y_2 = 9)\):
\(m = \cfrac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1}\)
\(m = \cfrac{9 - 10}{8 - 6}\)
\(m = \cfrac{-1}{2}\)
Therefore, we can determine that the slope is \(\boldsymbol{m = \cfrac{-1}{2}}\). Remember, a negative slope means the line is decreasing.
Rates of Change
A Rate of Change is a change in one quantity relative to the change in another quantity. It requires a unit such as kilometers per hour (or km/h).
When a relation is graphed, the slope describes the rate of change:
To find the slope of a line segment joining two points, subtract the \(y\)-values to get the rise and subtract the \(x\)-values in the same order to get the run. This is the same process used to determine the slope of an equation.
Example
A teenager can type \(240\) words every \(5\) minutes. What is the rate of change of typing speed?
We can determine the rate of change by using the slope formula:
\(\text{rate of change} = \cfrac{\Delta \text{words}}{\Delta \text{minutes}}\)
\(\text{rate of change} = \cfrac{240}{5}\)
\(\text{rate of change} = 48\)
Therefore, we can determine that the teenager can type at a speed of \(\boldsymbol{48\; [\textbf{words/minute}]}\).
A man can run \(850\) meters in \(10\) minutes.
We can determine the rate of change by using the slope formula:
\(\text{rate of change} = \cfrac{\Delta \text{distance}}{\Delta \text{minutes}}\)
\(\text{rate of change} = \cfrac{850}{10}\)
\(\text{rate of change} = 85 \; \left[\cfrac{\text{meters}}{\text{minute}}\right]\)
Therefore, we can determine that the man can run at a speed of \(\boldsymbol{85\; \left[\cfrac{\textbf{meters}}{\textbf{minute}}\right]}\).
The price of milk increases from \($34\) to \(54\) over the course of \(8\) years.
First, we can determine how much the price of milk has increased:
\(= 54 - 34\)
\(= 20\)
Next, we can determine the rate of change by using the slope formula:
\(\text{rate of change} = \cfrac{\Delta \text{price}}{\Delta \text{years}}\)
\(\text{rate of change} = \cfrac{20}{8}\)
\(\text{rate of change} = $2.5/\text{year}\)
Therefore, we can determine that the price of milk has increase at a rate of \(\boldsymbol{$2.5\;/\textbf{year}}\).